Soil microbial community responses to labile organic carbon fractions in relation to soil type and land use along a climate gradient
Abstract
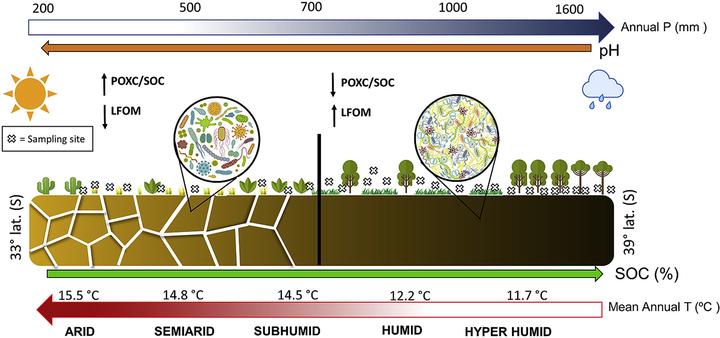
There has been a growing interest in studying the labile C pool in order to promote the sequestration and stabilization of soil organic carbon (SOC). Although labile SOC fractions have emerged as standardized indicators because of their potential to detect early SOC trends over time, the relationships between microbial attributes and labile SOC remains poorly understood. In this study, we explored the influence of labile SOC fractions on the topsoil bacteria-archaea community across 28 sites with different land use, climate aridity, and soil types across a wide range of SOC content (0.6–12%) in central Chile. We applied Illumina sequencing to the 16S rRNA to examine shifts in the diversity and composition of these soil microbial communities. Additionally, labile SOC fractions such as the permanganate oxidizable carbon (POXC) and light fraction organic matter (LFOM), along with the soil physicochemical properties were analyzed. The results demonstrated that among all of the environmental factors tested, the pH, POXC/SOC ratio and LFOM were key drivers of microbial community structure (beta-diversity). The alpha-diversity metrics exhibited a decreasing trend when aridity increased, and community structure was found to vary, with high POXC/SOC in sites associated with drier conditions. In addition, POXC/SOC ratios and LFOM were clearly related to shifts in the relative abundances of specific taxonomic groups at genera level. When there was high POXC/SOC and low LFOM content, members of Bacteroidetes (Adhaeribacter, Flavisolibacter, and Niastella), Proteobacteria (Skermanella, Ramlibacter, and Sphingomonas), and Archaea (Thaumarchaeota) were found to be the most dominant groups; however, the microbial taxa responded differently to both labile C fraction types. These results have implications for understanding how labile C content can potentially be used to predict shifts in the microbial community, thus facilitating the development of predictive ecosystem models, as well as early warning indicators for soil degradation.